Culture, being a cornerstone of human civilization, presents itself in a variety of ways across the world.Western vs Eastern Culture shine in this rich fabric, each contributing various hues to the global mosaic.
Even though we all come from the same place, our cultures can be very different. Western and Eastern cultures have their own ways of looking at things like how societies work, what’s important, how we talk to each other, and the things we do.
Firstly, Looking at these western culture vs eastern culture differences helps us understand how everything fits together in our world.
Think of human culture as a big, colorful blanket made up of traditions, beliefs, and habits. Western and Eastern cultures are like two big sections of this blanket. Each one has its own unique identity and has influenced everything from how people act to the art they create.
On the whole, eastern vs western culture have contributed greatly to making our world diverse and fascinating by exploring their differences.
What is the Difference Between The Eastern and Western Culture?
Values and Philosophies: Western vs Eastern Culture
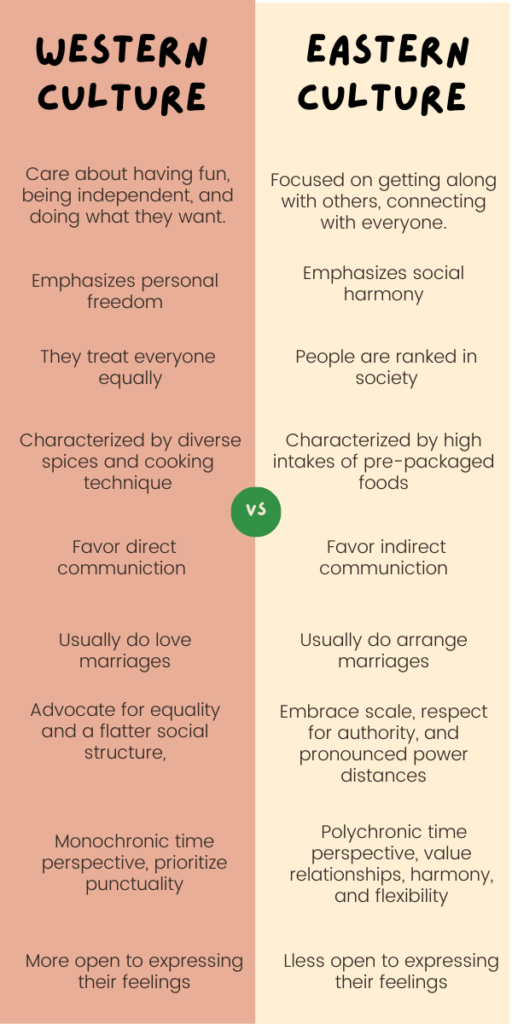
In Western culture, which comes from ancient Greece and Rome, people really care about having fun, being independent, and doing what they want. They also think it’s important to use reason and ask questions. Western culture is all about individual achievement, competition, and self-expression.
On the other hand, Eastern cultures are more focused on getting along with others, connecting with everyone, and finding balance influenced by Confucianism, Buddhism, Taoism, and Hinduism. They value things like respecting family, taking care of the community, and finding peace within oneself. Eastern cultures are known for being humble, listening to elders, and making sure everyone gets along.
Moreover, while Western culture emphasizes personal freedom, Eastern cultures prioritize social harmony. Additionally, Western societies highlight individual accomplishment, whereas Eastern cultures value community well-being. Furthermore, Western thought is characterized by the pursuit of pleasure, while Eastern cultures emphasize spiritual enlightenment.
Social Structures and Relationships
People in Western societies usually treat everyone equally and believe everyone should have a fair shot. If you work hard, you can move up in society, and they celebrate when someone does something great. People in the West often talk to each other in a casual way and are okay with sharing personal things.
On the other hand, in many Eastern cultures, the way people are ranked in society and family is really important. The older generation believes it’s important to respect previous generations. In these cultures, it’s more important for everyone to get along than for one person to say what he or she wants. In order to keep everyone happy, sometimes they prefer to talk in a roundabout way.
Moreover, while Western societies value equality and meritocracy, Eastern cultures prioritize respect for authority. Additionally, Western culture celebrates individual achievements, whereas Eastern cultures emphasize group harmony. Furthermore, Western communication tends to be direct, while Eastern cultures may prefer indirect communication to maintain social balance.
Cultural Expressions
The arts and literature in Western culture often reflect a celebration of individualism and self-expression. Genres like Renaissance art, Romantic literature, and contemporary pop culture showcase the Western penchant for exploring personal narratives and pushing artistic boundaries.
Traditional Eastern art forms, such as calligraphy, tea ceremonies, and traditional music, often embody a sense of disciplined refinement and attention to detail. The emphasis on symbolism and conveying deeper meanings can be observed in various Eastern art forms. Additionally, storytelling in Eastern cultures may prioritize moral lessons and allegories.
Cuisine and Lifestyle
Western cuisine is diverse, reflecting the multicultural nature of many Western societies. Individual preferences and dietary choices are highly valued. The fast-paced lifestyle in many Western countries often leads to convenience-oriented eating habits.
Eastern cuisine, characterized by diverse spices and cooking techniques, often reflects a connection with nature and an emphasis on balance. Mealtime is often a communal affair, reinforcing social bonds. Eastern lifestyles may place greater importance on mindfulness and balance, with practices like meditation and yoga originating from these cultures gaining global popularity.
Social Behavior
There is a fundamental disparity in social behavior in Western societies, where individualism, directness, and assertiveness are praised. Meanwhile, Eastern cultures place a premium on collective harmony, embracing indirect communication to sidestep conflict.Western vs Eastern Culture this divergence in approach shapes interpersonal relationships and societal dynamics, portraying the rich diversity within the global human experience.
Western societies celebrate personal achievement, independence, and self-expression, encouraging a fast-paced, individualistic lifestyle. Conversely, Eastern cultures prioritize family, community, and communal harmony, enabling a more relaxed and family-oriented way of life. This stark contrast in lifestyle underscores the multifaceted nature of human existence across cultures.
Beliefs and Values
Divergent belief systems form another frontier in the Western vs Eastern Culture. Western cultures emphasize personal freedom, democracy, and human rights, while Eastern cultures uphold social harmony, duty, and respect for authority. The differing philosophical foundations shape the moral compasses guiding individuals in each cultural sphere.
Communication Style
Communication becomes a lens through which we observe another layer of dissimilarity. Western cultures favor direct contact, while Eastern cultures rely on indirect expression and nonverbal cues. This divergence reflects varying approaches to conveying messages and the importance of interpersonal harmony within each cultural context.
Finding Common Ground
Whether there can be similarities between Eastern and Western culture sparks contemplation. While significant differences exist, encouraging mutual understanding is essential. Cultural disparities, such as diverse religions, clothing, rituals, and ideologies, present formidable barriers.
Elders as Decision-Makers
An intriguing contrast lies in the role of elders. In Eastern cultures, elders wield authority, and decisions are often made without question. In the West, the responsibility for elderly care may extend to the state, marking a distinction in the approach to familial roles and responsibilities.
Education Disparities
Education stands as a microcosm of Western vs Eastern Culture. Western education prioritizes creativity and individual development, encouraging active participation. Conversely, Eastern education, with a more authoritative teaching approach, links achievement to hard work. The integration of special needs students further highlights disparities in educational practices.
Individualism vs. Collectivism
A foundational difference between Western vs Eastern Culture lies in the orientation toward individualism and collectivism. Western cultures champion individual freedom and personal achievement, rooted in European traditions. Conversely, Eastern cultures, particularly in Asia, prioritize collective harmony and familial ties, encouraging a strong sense of interconnectedness. This dichotomy shapes societal values, with Eastern cultures emphasizing group needs over individual aspirations.
Social Hierarchy and Power Distance
The perception of social hierarchy and power distance varies markedly. Western societies advocate for equality and a flatter social structure, while Eastern cultures often embrace scale, respect for authority, and pronounced power distances. This hierarchical framework permeates family dynamics, workplace interactions, and societal protocols, influencing daily life.
Time Orientation
Divergent approaches to time orientation characterize Eastern and Western culture. Western cultures, with a monochronic time perspective, prioritize punctuality and efficiency. In contrast, many Eastern cultures, influenced by a polychronic time perspective, value relationships, harmony, and flexibility. This contrast manifests in fluid schedules and adaptability based on interpersonal dynamics.
Spirituality and Religion
In Eastern and Western culture, spirituality and religion play different roles. Spirituality is often an individualistic pursuit in Western societies, influenced by Judeo-Christian traditions, allowing for diverse beliefs. In contrast, Eastern cultures emphasize rituals, collective worship, and a solid connection to ancestral traditions. Self-realization and harmony with the universe are at the heart of Eastern spiritual practices like Buddhism and Hinduism.
Culture’s Influence on Design: Western vs Eastern Culture

The cultural tapestry profoundly influences human creativity, shaping architects, artists, and everyday objects. It emphasizes harmony and interdependence in Eastern design, while Western design highlights simplicity and individuality, reflecting distinct worldviews, values, and aesthetics.
Take a Look at the profound impact of culture on design and discover how Eastern and Western perspectives differ.
Philosophical Underpinnings: Western Vs Eastern Culture
Eastern Design:
Rooted in philosophies such as Confucianism, Taoism, Buddhism, and Hinduism, Eastern design places a premium on harmony, balance, and the interconnectedness of all things. Nature is a profound source of inspiration, emphasizing the essence of simplicity and tranquillity. Elements such as flowing lines, natural materials, and symbolic motifs are prevalent, encouraging a sense of spiritual connection.
Western Design:
Western design, on the other hand, often draws from Greco-Roman traditions and Enlightenment philosophies. Individualism, rationality, and the celebration of human achievement are central themes. Structures and objects in Western design may embody a sense of grandiosity, symmetry, and a focus on functionality. The aesthetics lean towards clean lines, geometric precision, and an appreciation for technological innovation.
Color Palette and Symbolism : Western Vs Eastern Culture
Eastern Design:
Many Eastern designs choose colours for their cultural and symbolic significance, frequently incorporating red to symbolize luck and prosperity in various Eastern cultures.
These designs embed deep symbolism, carrying cultural meanings through motifs like dragons, cranes, and lotus flowers, while gold reflects wealth and black and white are chosen to represent balance and harmony.
Western Design:
In Western design, color choices may prioritize aesthetic preferences over symbolic meanings. Neutral tones and muted colors are familiar, emphasizing sophistication and versatility. While symbolism exists, it tends to be more subtle and context-dependent, allowing for a broader range of interpretations.
Spatial Concepts: Western Vs Eastern Culture
Eastern Design:
In the East, rooms blend with nature. Think of Japanese houses as a mix of inside and outside. They follow Feng Shui to keep good.
Western Design:
In the West, rooms are separate. Each space has its own job. It’s about making things organized and valuable.
Cultural Adaptation and Fusion: Western Vs Eastern Culture
In a global society, design frequently transcends cultural boundaries, creating a fusion of Eastern and Western ideas. Cultural diversity leads to fusion styles, which blend features from both areas seamlessly.
Conclusion:Western vs Eastern Culture
Western and Eastern culture appear to be opposed; however, these are only generalizations. The world is always changing and different in many ways. It keeps getting new things and ideas. When we understand and like all the different cultures, we learn more about how people live in our connected world. When we see how different everyone is, we can understand them better and see how they are just like us.